Hydrazine
(anhydrous), H2NNH2, is a clear, fuming,
corrosive liquid with an ammonia-like odor; melting at 1.4 C, boiling at 113.5
C, specific gravity 1.011. It is very soluble in water and soluble in alcohol.
It decomposes on heating or exposure to UV to form ammonia, hydrogen, and
nitrogen, which may be explosive with a blue flame when catalysed by metal
oxides and some metals such as platinum or Raney nickel. It is prepared from
ammonia with chloramine in the presence of glue or gelatin (to inhibit
decomposition of the hydrazine by unreacted oxidants) as the hydrate form
usually (100% monohydrate contains 64% by weight hydrazine). Hydrazine is also
prepared from sodium hypochlorite with urea in the presence of glue or gelatin.
Botht ammonia and amines are nitrogen nucleophiles which donate electrons (they
are Lewis bases). But hydrazine (diamine) has much stronger nucleophilicity
which makes it more reactive than ammonia. Hydrazine has dibasic and very
reactive properties. Hydrazine is used as a component in jet fuels because it
produce a large amount of heat when burned. It is less flammable and less
volatile than hydrocarbon fuels. It is relatively environmentally friendly
because they degrade quickly in the environment. Hydrazine is used as an oxygen
scavenger for water boiler feed and heating systems to prevent corrosion damage.
Hydrazine is used as a reducing agent for the recovery of precious metals. It is
used as a polymerization catalyst and a chain extender in urethane coatings. It,
or a derivative thereof, is versatile intermediate. They have active
applications in organic synthesis for agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals,
photographic, heat stabilizers, polymerization catalysts, flame-retardants,
blowing agents for plastics, explosives, and dyes. Recently, hydrazine is
applied to LCD (liquid crystal displays) as the fuel to make faster thin-film
transistors. Hydrazone is a compound containing the group
-NH·N:C-. It is formed from a condensation reaction aldehydes or ketones with
hydrazines (commonly phenylhydrazine). It is used as an exotic fuel. Aromatic
hydrazones are used to form indole by a ring closure reaction (Fischer
synthesis). Hydrazones and hydrazines are converted to aldehydes and ketones to
corresponding hydrocarbons by heating the carbonyl compound with sodium ethoxide
(Wolf-Kishner reduction). Azide contains the group -N3
represented as a resonance hybrid of two structures,
-N-N-��N+ ��
-N=N+=N-. Organic azides are
compounds replaced by a hydrocarbon group as in alkyl or aryl from hydrazoic
acid (HN3)and have general
formula RN3. Acyl azide is a
compound in which the hydroxy group of a carboxylic acid is replaced by the
azido group (HN3). Hydrazide is an acyl
hydrazine. Acyl (-CO) is an organic radical formed by removal of a hydroxyl
group from an organic acid (carboxyl group). Organic azides are
useful for the synthesis of target compounds. They act as electrophiles on the
nitrogen attached to the carbon and have electron-donating character for the
neighboring carbon.
Sulfonic acid is a compound with general formula RSO2OH, where R is an aliphatic
or aromatic hydrocarbon. It is a derivative of sulfuric acid (HOSO2OH) where an
OH has been replaced by a carbon group or a compound where a hydrogen atom has
been replaced by treatment with sulfuric acid; for example, benzene is converted
to benzenesulfonic acid (water-soluble). Sulfonic acid has a sulfur atom bonded
to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon and bonded also to three oxygen atoms, one of
which has been attached to a hydrogen atom. Sulfonic acid is acidic due to the
hydrogen atom, stronger than a carboxylic acid. Sulfonic acid is one of the most
important organo sulfur compounds in organic synthesis. Sulfonic acids are used
as catalysts in esterification, alkylation and condensation reactions.
Sulfonates are salts or esters of sulfonic acid. Sulfonic salts are soluble in
water. Sulfonic acid and its salts present in organic dyes provide useful
function of water solubility and or improve the washfastness of dyes due to
their capabiltity of binding more tightly to the fabric. They are widely used in
the detergent industry. Alkylbenzene sulfonic acid is the largest-volume
synthetic surfactant because of its relatively low cost, good performance, the
fact that it can be dried to a stable powder and the biodegradable environmental
friendliness. Sulfonate cleaners do not form an insoluble precipitates in hard
water. Sulfonic acid salts and esters are intermediates widely used in organic
synthesis and particularly phenolic compounds and cation exchange resins. They
are synthetic intermediate for a number of biologically active compounds and
pharmaceutical candidates such as sulfa drugs.
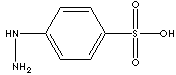
4-Hydrazinobenzenesulfonic
Acid is used as an intermediate to manufacture
pharmaceuticals, dyes and other organic
synthesis.
|